

The name counts the total number of carbon atoms in the longest chain - including the one in the carbonyl group. Ethanal, for example, is written as CH 3CHO methanal as HCHO. That could easily be confused with an alcohol. When you are writing formulae for these, the aldehyde group (the carbonyl group with the hydrogen atom attached) is always written as -CHO - never as COH. All that differs is the complexity of the other group attached. Notice that these all have exactly the same end to the molecule. I'm just trying to avoid adding to your confusion! It is just that if you are fairly new to organic chemistry you might not have come across any compounds with benzene rings in them yet.

Note: There is no very significant reason for this. Or, more commonly, a hydrocarbon group which might be an alkyl group or one containing a benzene ring.įor the purposes of this section, we shall ignore those containing benzene rings. In aldehydes, the carbonyl group has a hydrogen atom attached to it together with either
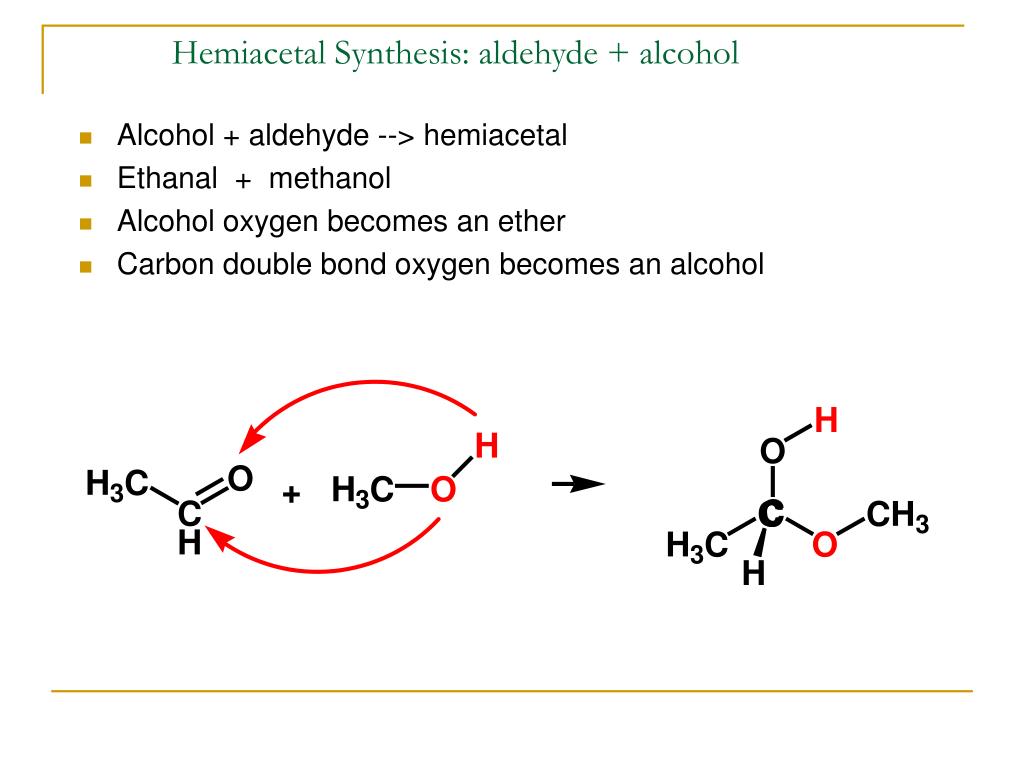
They are simple in the sense that they don't have other reactive groups like -OH or -Cl attached directly to the carbon atom in the carbonyl group - as you might find, for example, in carboxylic acids containing -COOH. Details of the chemical reactions of aldehydes and ketones are described on separate pages.Īldehydes and ketones as carbonyl compoundsĪldehydes and ketones are simple compounds which contain a carbonyl group - a carbon-oxygen double bond. It also considers their simple physical properties such as solubility and boiling points. This page explains what aldehydes and ketones are, and looks at the way their bonding affects their reactivity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
